August 30, 2024
-
- About UsMā mātou
- Our ScienceTe pūtaiao
- Future Landscapes Ngā Horanuku AnamataIn the future, landscapes will contain mosaics of land use that are more resilient, healthy and prosperous than today.
- Assessing Contaminants with Stream Order
- Benign Denitrification in Groundwaters
- Cascade of Soil Erosion
- Connecting Soil and Water Quality
- Crop Disease Under Climate Change
- Faecal Source Tracking
- Healthy Estuaries
- Innovative Agricultural Microbiomes
- Interoperable Modelling
- Land Use for Nutritious Diets
- Land Use Opportunities
- Land Use Suitability
- Linking Legacies to Wai
- Mapping Freshwater Contaminants
- Matarau: Empowering Māori Landowners in Land Use Decisions
- Measuring Denitrification
- Monitoring Freshwater Improvement Actions
- Mosaic vs Monoculture Landscapes
- Next Generation Systems
- Pasture for Humans
- Peri-Urban Potential
- Phosphorus Best Practice
- Physiographic Environments of New Zealand
- Pohewa Pae Tawhiti
- Protein Future Scenarios
- Silvopastoral Systems
- Sources and Flows
- Visualising Forestry Harvesting Cycles
- Incentives for Change Ngā Poapoa PanoniWe want to reward New Zealand’s primary producers for producing high-value products in sustainable ways.
- Aotearoa Food Cultures
- Appropriate Use of Taonga Species
- Credence Attributes On Farm
- Early Māori Agricultural Entrepreneurship
- EU Green Deal: Impact on NZ Exports
- Eutrophication Product Footprinting
- Impact of Imported Feed Shortages
- Incentives for Data Sharing
- Indicators Working Group
- Integrating Value Chains
- Kaitiaki Intelligence Platforms
- Kuaha Matihiko: Digital Gateway
- Measuring Full Impacts of Land-Use Change
- New Models of Collective Responsibility
- Options for Rural Investment
- Reasons for Water Quality Improvement
- Regenerative Agriculture
- Register of Land Management Actions
- Rewarding Sustainable Practices
- Signals for Land Stewards
- The Matrix of Drivers
- Workforce Implications of Land-Use Change
- Pathways to Transition Ngā Ara WhakawhitiWe are growing understanding of what it takes to transition to resilient, healthy and prosperous futures, and are developing tools to help.
- Connecting Food Producers & Consumers
- Diverse Experiences of Farming
- Enhancing Assurance Schemes
- Future Scenarios for Arable Agriculture
- Implementing Te Mana o Te Wai
- Land-Use Scenarios for Nikau Farm
- Lessons from Our Land and Water
- Mauri Whenua Ora
- Ngā Tai-o-Rongo
- Predicting Agricultural Research Adoption
- Retiring Farmland into Ngahere
- Revitalise Te Taiao
- Rural Professionals Fund 2020–21
- Rural Professionals Fund 2021–22
- Rural Professionals Fund 2022–23
- Rural Professionals Fund 2023–24
- Science in Freshwater Policy Development
- Shared Vision for Land Use in Marlborough
- Storying Kaitiakitanga
- Synthesis Scenarios for Future Land Use
- The Collaboration Lab
- Trust and Social Licence
- Urban-Rural Partnerships for Equal Change
- Whenua Life Values
- Future Landscapes Ngā Horanuku AnamataIn the future, landscapes will contain mosaics of land use that are more resilient, healthy and prosperous than today.
- News + EventsHe pānui
- Resources Ngā rauemi
- View by topic
- Climate Change
- Collaboration
- E.coli
- Farm Environment Plans
- Farm Management
- Farming for Good
- Increasing Value
- Irrigation
- Land-Use Change
- Measuring Water Quality
- Mitigation
- Nitrogen
- NPS-FM
- Nutrient Management
- Phosphorus
- Regenerative Agriculture
- Sector Transformation
- Sediment
- Social Licence
- Te Ao Māori
- Te Mana o Te Wai
- Winter Grazing
- View by topic
- Outcomes Ngā puawaitanga
Resources related to
E.coli
Charles Farmer, PIXNIO
You are here: Home Topics E.coli
Summer swims in a lake or river are an important part of Kiwi culture – but to be safe, the presence of E.coli (Escherichia coli) bacteria has to be minimised. These resources aim to reduce farm sources of E.coli and improve its detection.
Showing 1 - 12 of 134 results
Technical Report
Net export of E. coli from the Toenepi wetland cannot be explained by growth of naturalized E. coli in the water column
Runoff from agricultural land is recognized as an important source of contaminants—nitrogen, phosphorus, sediment and Escherichia coli—that impact water quality. Constructed wetlands have been promoted…
Technical Report
eDNA as a holistic measure of pastoral landscape effects on taonga species
Freshwater quality is measured with key indicators such as faecal indicator bacteria (E. coli), nitrates and phosphates. For communities, such indicators are vague and somewhat…
Summary
Study Shows Dairy Farm Work is Helping Improve Water Quality
The implementation of Good Management Practices on-farm does improve water quality, proves new research that analysed water quality trends over 20 years. As part of…
Guidance
Excluding stock from smaller streams
This factsheet is for farmers, industry bodies and regional authorities developing regional freshwater policy. Most of the contaminant load in waterways across New Zealand originates…
Technical Report
Nitrogen, phosphorus, sediment and Escherichia coli in New Zealand’s aquatic receiving environments: Comparison of current state to national bottom lines
This report is the first assessment of where ‘bottom lines’ for contaminants are exceeded across Aotearoa. It reveals the size of job required to achieve…
Video
Monitoring Freshwater Improvement Actions webinar
This webinar explains an interactive WebApp that helps detect improvements in rivers, lakes and groundwater, and helps select appropriate monitoring technologies that enable early detection…
Interactive Tool
Monitoring Freshwater Improvement Actions Webapp
These WebApp tools will help freshwater stewards and kaitiaki decide what to measure, where, when, with what technology, and understand how much it will cost.…
Journal Article
High-resolution genomic analysis to investigate the impact of the invasive brushtail possum (Trichosurus vulpecula) and other wildlife on microbial water quality assessments
Escherichia coli are routine indicators of fecal contamination in water quality assessments. Contrary to livestock and human activities, brushtail possums (Trichosurus vulpecula), common invasive marsupials in…
Journal Article
Draft genome sequences of Escherichia spp. isolates from New Zealand environmental sources
Escherichia coli is often used as a fecal indicator bacterium for water quality monitoring. We report the draft genome sequences of 500 Escherichia isolates including newly described Escherichia species, namely Escherichia…
Summary
Delineating the interaction of Escherichia species with freshwater pathogens and land-use
A project to add value to Ministry for the Environment’s Freshwater Pathogen QMRA study found that low numbers of E. coli phylotype B1 and a…
Interactive Tool
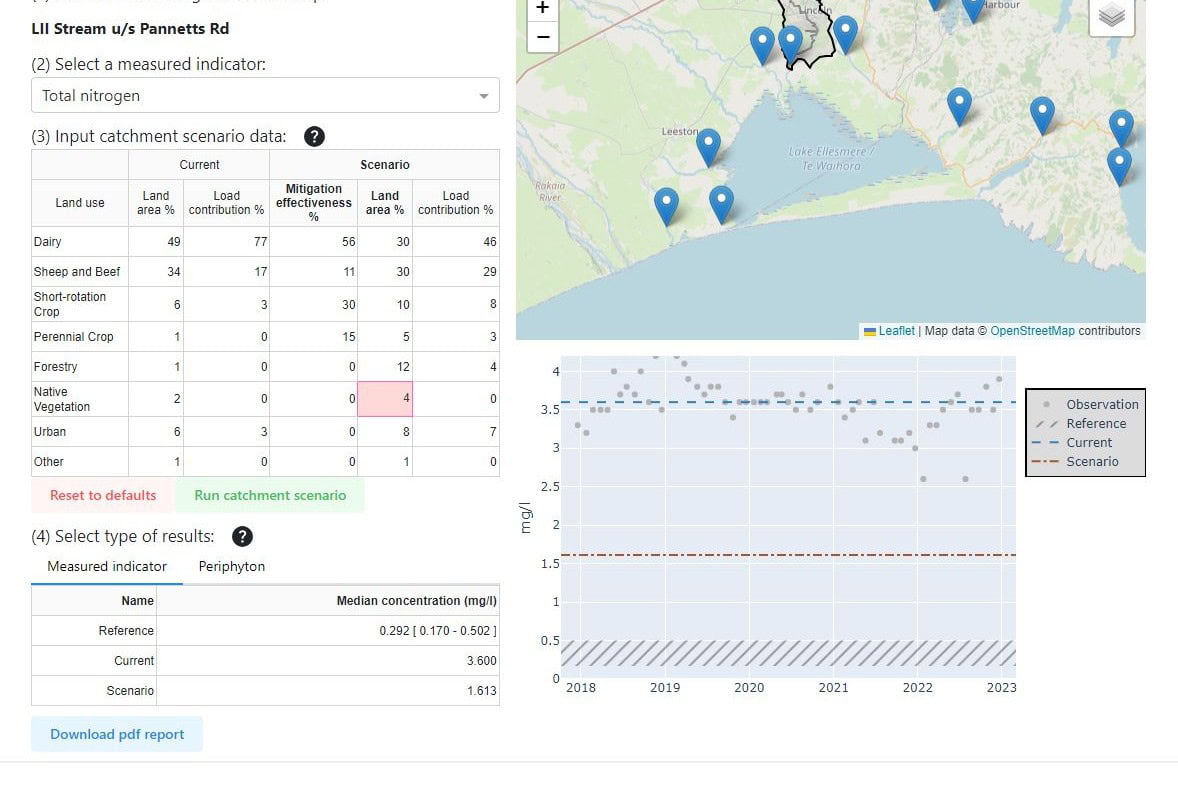
Freshwater Improvement Scenario Builder
The Freshwater Improvement Scenario Builder is a tool for exploring the effect of mitigation strategies and land use change on water quality. It shows the…
Guidance
Monitoring E. coli in lakes and rivers
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a common bacteria found in the digestive system of warm-blooded animals, including humans. Because E. coli can survive for a…
 View Our Strategy Document 2019 – 2024
View Our Strategy Document 2019 – 2024