Shade From Trees Inhibits Pasture Growth
A trial designed to test whether pasture production would increase in a shaded environment showed the opposite
Waikato dairy farmer Graham Smith has been growing Paulownia trees on his farm for 30 years. He reckons he could just about survive on the income from timber alone now without relying on the returns from his 80 cows.
“My son is coming back here soon to take over the farm. I’m going to live off the timber and he’s going to live off the dairying,” Graham says.
While Graham was planting trees, Regan McCorquindale, LIC FarmWise consultant, was growing up on a neighbouring farm and saw what was happening on the Smith family property, called Miraka Farm.
“I’d always known he’d been growing these funny looking trees. I started to learn more about them when I had a pasture measuring business and Graham was one of my clients,” Regan recalls.
He really started to take notice during the drought of summer 2019 when about the only grass growing in the district seemed to be under the trees in Graham’s paddocks. “All the pasture under the trees was still growing, whereas everything else was more like cardboard, just absolutely dead.”
It occurred to him that growing more trees on farms could help make them summer-safe, so with Our Land and Water Rural Professionals Fund support, Regan set up a trial to put some real numbers behind that theory. He also wanted to compare cow behaviour under shade and away from shade.
A trial over multiple years would capture greater variation in weather conditions and give more reliable results
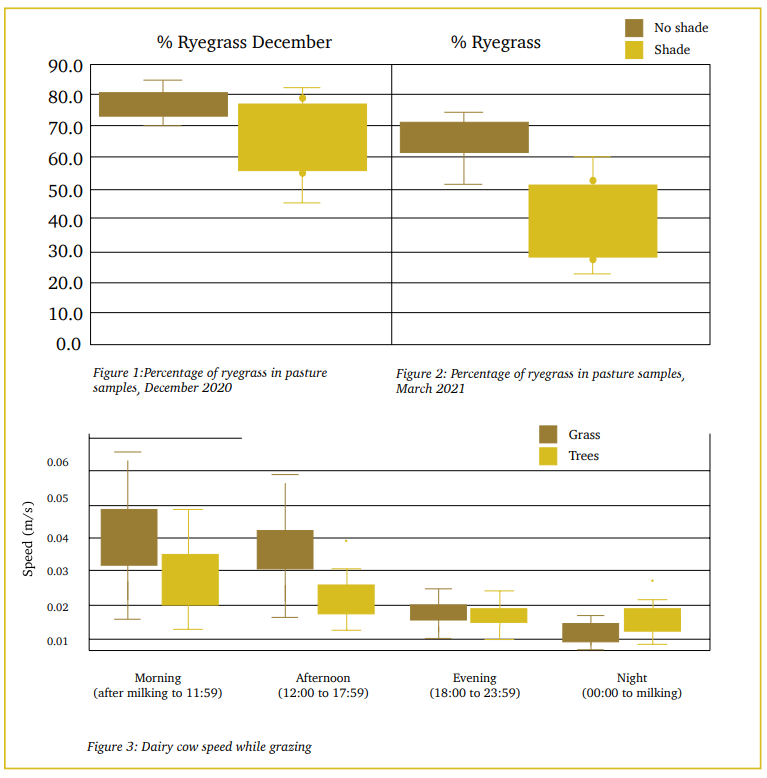
However, the trial in fact showed unshaded pasture grew better than shaded. Pasture monitoring was done in December 2020 and then again in March 2021. The December pasture samples showed a greater percentage of ryegrass in the ‘no shade’ trial site (see Figure 1) and that pattern continued in March (see Figure 2).
The data collected shows the clover percentage was higher in December in the shade. Crude protein level is the only valuable metric under a ‘shade’ paddock that has more advantageous results compared to the ‘no shade’ paddocks. All the other metrics were similar, or in favour of the ‘no shade’ paddocks.
Dense planting
Graham says the trial results confirmed what experience had already told him – that trees in the trial block were planted too densely to allow pasture to thrive.
“I could see it myself before they did the trial that I was having trouble with the pasture, so my plans for this summer are to thin the trees down from about 100 trees/ ha to 50 and let more sunlight in to rectify the problem,” he says.
Regan agrees that thinning the trees to let in more light will be helpful. Graham is sure of the value of trees, but is still working out exactly where the sweet spot is for the ratio of trees to pasture. “You’ve got to stay flexible and roll with the punches. I’m still learning and so is everybody else,” he says.
“You get to the stage where you say, ‘Am I in trees or dairy?’, but I want to keep the blend because I think diversification is the name of the game,” says Graham. “You don’t want to have everything tied up down one track. I think that’s a smarter move than being tied into one form of farming.”
Cow behaviour
The second part of the project assessed cow behaviour in shaded versus unshaded environments.
The cows were split into two herds and fitted with Cow Manager ear tags, HOBO cow collars and GPS pedometers. The cows with access to shade moved faster than those who were more protected by shade from the trees during the afternoon (see Figure 3). The activity collars also showed that the cows in the no shade paddocks spent more time lying down than those in the shaded trial area.
Next steps
The summer and autumn of 2021 received a lot more rain than has been typical in recent years. A trial over multiple years would capture greater variation in weather conditions and give more reliable results. The optimal number of stems per hectare that offer shade to cows and allow an increase in pasture production through drier summers is still to be found.
– Tony Benny for Our Land and Water National Science Challenge
More information:
- Rural Professionals Fund 2020-21
- Download PDF
- All text in this article is licensed for re-use under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Author
2 responses to “Shade From Trees Inhibits Pasture Growth”
I have thinned the trees but will need to do more thinning yet I think. There is considerably less shade now and I think the pasture will respond. I still have enough trees to claim carbon credits and to mill for timber. I have also started baling the autumn leaf fall. My first attempt gave an ME of 6 which was a consequence of a slow leaf fall compered to normal and therefore an extended harvest period which caused some leaf deterioration.
Regan’s observation of the greening effect of trees in a drought is real and it does have benefits when it does rain with substantially faster regrowth.
I also noticed that the trees caused most of the C4 grasses to disappear due to a lack of light and warmth.
Although I lost grass growth I have done well from the thinning of the trees. I felled three per day which took the cows about 20 minutes to clean up. That is leaves, small sticks and bark. I also retrieved some good trunks for milling and saved a load of silage per day.
I think taking the good with the bad I will be somewhere near break even, and it was a good brain workout.Well done Graham, that is an interesting piece of work. I wonder if you tracked the milk output of the cows in the shade vs those without access to shade, as well as the productive average age of each herd, if you would find more benefits?
 View Our Strategy Document 2019 – 2024
View Our Strategy Document 2019 – 2024



Leave a Reply